The Pythagorean triganometric identity
\[\sin^2\theta + \cos^2\theta = 1\]Proof:
In this right triangle …
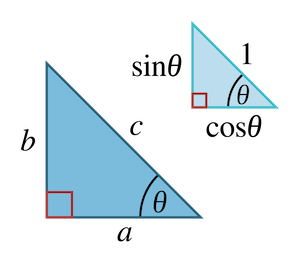
Pythagoras’ Theorem states that \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\). Dividing both sides by \(c^2\) then gives us \(\frac{a^2}{c^2} + \frac{b^2}{c^2} = 1\). Since the definitions of \(\sin\theta\) and \(\cos\theta\) are, respectively, \(\frac{b}{c}\) and \(\frac{a}{c}\), the above identity follows immediately.
QED.
Angle sum and difference identities
\[\sin(\alpha \pm \beta) = \sin\alpha\cos\beta \pm \cos\alpha\sin\beta\] \[\cos(\alpha \pm \beta) = \cos\alpha\cos\beta \mp \sin\alpha\sin\beta\] \[\tan(\alpha \pm \beta) = \frac{\tan\alpha \pm \tan\beta}{1 \mp \tan\alpha\tan\beta}\]Proof:
Consider the following …
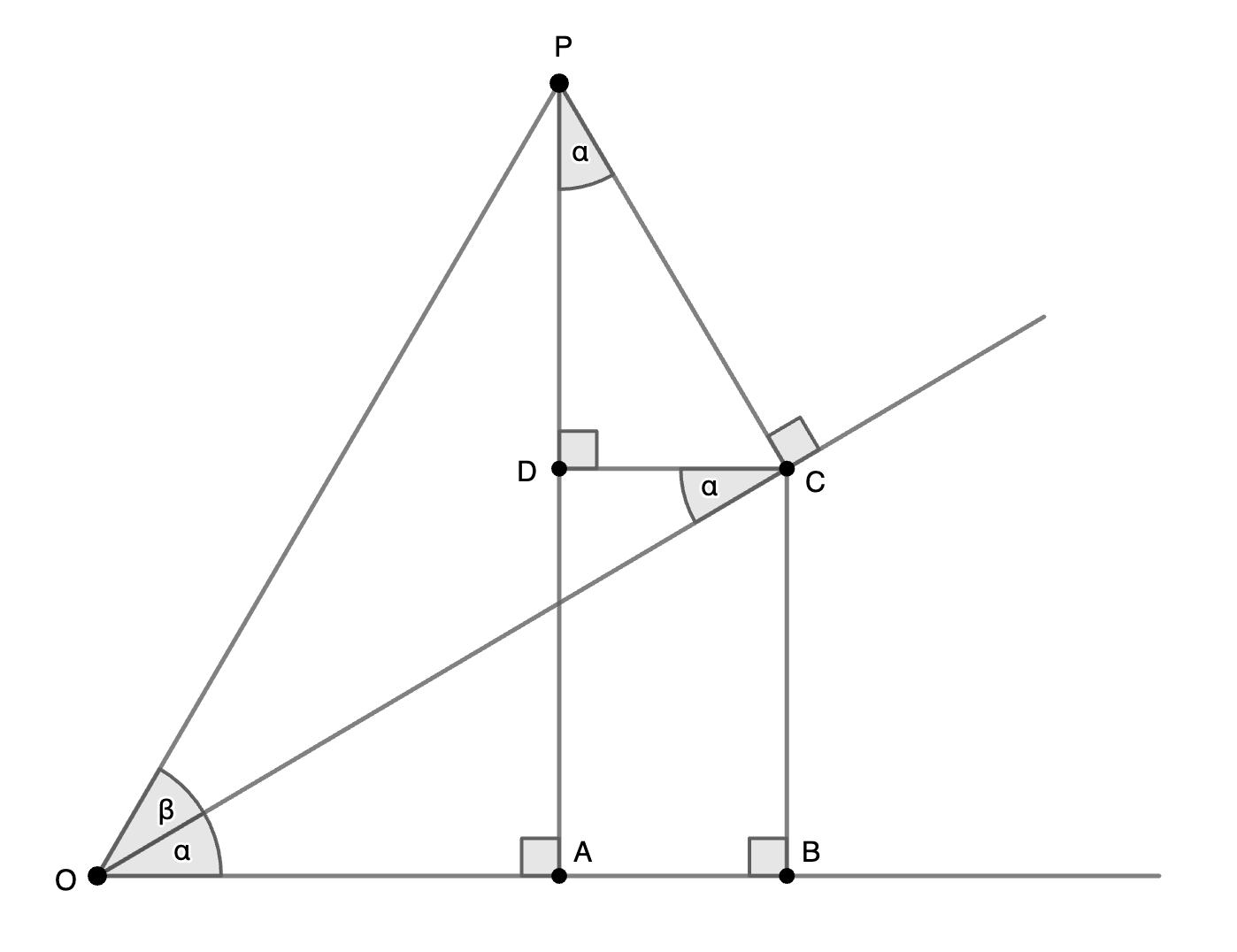
Here …
\[\sin\alpha = \frac{BC}{OC} = \frac{DC}{PC}\] \[\sin\beta = \frac{PC}{OP}\] \[\cos\alpha = \frac{OB}{OC} = \frac{DP}{PC}\] \[\cos\beta = \frac{OC}{OP}\] \[\sin(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{AP}{OP} = \frac{AD + DP}{OP} = \frac{BC + DP}{OP} = \frac{BC}{OP} + \frac{DP}{OP} = \frac{BC}{OC}\frac{OC}{OP} + \frac{DP}{PC}\frac{PC}{OP} = \sin\alpha\cos\beta + \cos\alpha\sin\beta\] \[\cos(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{OA}{OP} = \frac{OB - AB}{OP} = \frac{OB - DC}{OP} = \frac{OB}{OP} - \frac{DC}{OP} = \frac{OB}{OC}\frac{OC}{OP} - \frac{DC}{PC}\frac{PC}{OP} = \cos\alpha\cos\beta - \sin\alpha\sin\beta\]If we substitute \(-\beta\) for \(\beta\) in the above then we get …
\[\sin(\alpha + -\beta) = \sin\alpha\cos(-\beta) + \cos\alpha\sin(-\beta)\] \[\cos(\alpha + -\beta) = \cos\alpha\cos(-\beta) - \sin\alpha\sin(-\beta)\]But we know that \(\cos(-\beta) = \cos\beta\) and \(\sin(-\beta) = -sin\beta\) and so …
\[\sin(\alpha -\beta) = \sin\alpha\cos\beta - \cos\alpha\sin\beta\] \[\cos(\alpha -\beta) = \cos\alpha\cos\beta + \sin\alpha\sin\beta\]Now, since …
\[\tan\alpha = \frac{\sin\alpha}{\cos\alpha}\]Then …
\[\tan(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{\sin(\alpha + \beta)}{\cos(\alpha + \beta)} = \frac{\sin\alpha\cos\beta + \cos\alpha\sin\beta}{\cos\alpha\cos\beta - \sin\alpha\sin\beta}\]If we divide the top and bottom by \(\cos\alpha\cos\beta\) then we get …
\[= \frac{\frac{\sin\alpha\cos\beta}{\cos\alpha\cos\beta} + \frac{\cos\alpha\sin\beta}{\cos\alpha\cos\beta}}{\frac{\cos\alpha\cos\beta}{\cos\alpha\cos\beta} - \frac{\sin\alpha\sin\beta}{\cos\alpha\cos\beta}}\] \[= \frac{\frac{\sin\alpha}{\cos\alpha} + \frac{\sin\beta}{\cos\beta}}{1 - \frac{\sin\alpha\sin\beta}{\cos\alpha\cos\beta}}\] \[= \frac{\tan\alpha + \tan\beta}{1 - \tan\alpha\tan\beta}\]If we substitute \(-\beta\) for \(\beta\) in the above then we get …
\[\tan(\alpha + -\beta)= \frac{\tan\alpha + \tan(-\beta)}{1 - \tan\alpha\tan(-\beta)}\]But we know that \(\tan(-\beta) = -\tan\beta\) and so …
\[\tan(\alpha - \beta)= \frac{\tan\alpha - \tan\beta}{1 + \tan\alpha\tan\beta}\]QED.